Last updated: April 27, 2023
Any links on this page that lead to products on Amazon are affiliate links and I earn a commission if you make a purchase. Thanks in advance – I really appreciate it!
The other day, my neighbor asked me to check out a horse he was thinking of buying. As I took a closer look, I noticed some signs of Navicular Disease, and my neighbor started to worry if that would rule out the purchase altogether.
I recommended passing on the horse with navicular disease. It can be a severe and debilitating syndrome that the horse may never fully recover. Navicular syndrome is a degenerative bone disease in the heel of the horse’s feet, typically the front feet.
Choosing the perfect horse is a challenge. Whether you’re drawn to a horse’s unique color or impressive pedigree, it’s important to make sure that the animal is healthy and sound. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into Navicular Disease, a condition that affects many horses and can have significant implications for their well-being.
What Is Navicular Syndrome?
Navicular Disease is a multifaceted condition that impacts the navicular bone—a small yet essential bone in a horse’s hoof—and its surrounding structures. Specifically, this disease involves the gradual deterioration of the navicular bone situated at the rear of the coffin joint within the hoof.
As the bone degenerates, it causes soreness in the horse’s heel, leading to lethargic movement and lameness. The primary consequences of this condition include discomfort and lameness in the front feet, which can significantly affect a horse’s performance and overall well-being. Detecting this degenerative disease can prove challenging due to its often subtle and inconspicuous symptoms.

What Causes Navicular Disease?
While the exact cause remains unknown, experts believe it is multifactorial, involving genetics, conformation, and environmental factors. Horses with a genetic predisposition, such as Quarter Horses and Thoroughbreds, may be more prone to developing the condition. Additionally, conformational aspects like upright pasterns, small feet, and a large body mass can put added stress on the navicular bone, increasing the likelihood of Navicular Disease.
Environmental factors, including working on hard or uneven surfaces, can also contribute to the development of the disease. Inadequate hoof care, poorly fitted shoes, or excessive toe length can alter the biomechanics of the foot, increasing the strain on the navicular bone and the associated structures.
Symptoms of Navicular Disease
As a new horse owner, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the symptoms and signs of Navicular Disease. The primary indicator is lameness, which may be subtle or intermittent at first but may worsen over time. A horse with Navicular Disease may be reluctant to move forward, stumble, or take short, choppy strides.
A horse’s deteriorating navicular condition often starts with acute pain in the hoof. Of course, the horse lacks the ability for complex communication, so naturally, it can’t tell you what he’s feeling. So, you have to pay attention to the horse’s behavior and how it moves during its runs. Chronic forelimb lameness occurs more often in performance horses rather than in ones not stressed as much.
A horse with degenerated navicular bone expresses the condition by pointing one foot. It does this because, typically, the pain starts in one foot more acutely. When the animal runs, may stop often to rest and might alternate its weight from side to side. Horses may also switch lead legs when running, which can be an alarming symptom.
Since the heel is also degenerating, the horse typically lands toe-to-heel, contrasted with a healthy heel-to-toe landing, which the usual horse exhibits. Paying attention to the movements and overall condition of your horse will help you catch issues and plan possible treatment.
Other signs to look for include heat or swelling around the coronet band, uneven wear on the hoof wall or shoes, and a shortened stride when turning or moving on uneven ground. Remember that early detection is key to managing the condition effectively, so monitoring your horse closely for these signs can help ensure their long-term health and happiness.
The condition impacts horse’s feet in several ways:
- Significant degradation in the bone’s central cavity, where marrow is located.
- Damage to the cartilage fibers.
- Increased likelihood of new bone formation, sometimes known as medullary sclerosis.
- Pronounced displacement of tendons and flexor bone.
- Development of enthesophytes, or spurs, at the attachments of bones and ligaments. These abnormal bony outgrowths can cause discomfort in the horse.
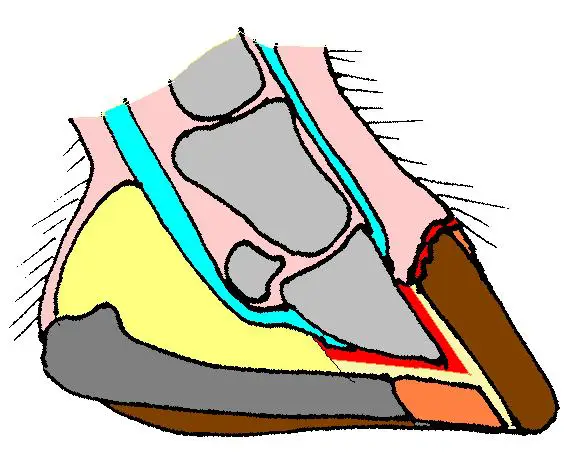
About the navicular bone
To have a better understanding of the disease, one first needs to understand more about the affected structure.
- Etymology: The prefix “navicu” comes from Latin and means a small boat. The reason for this prefix is because the shape of the navicular bone resembles a canoe (a pointed vessel used to navigate the seas)
- Structure: The navicular bone is a small, flattened bone lined across the back of a coffin joint. It comprises a central marrow cavity for nerves and blood vessels to enter and a smoother backside, which acts as a gliding surface for the flexor tendon.
- Location: The navicular bone is located within the horse’s hoof, between the coffin bone and the pastern bone. The navicular bone is surrounded by many soft tissues, which help attach the bone to other ligaments. A soft sac called the navicular bursa acts as a cushion to the bone.
- Function: The navicular bone’s primary function is to act as a gliding surface for the digital flexor tendon. It helps the tendon to switch the angles and allows for movement.
Now as we have a better understanding of the structure and what it does, let’s look at the symptoms associated with navicular bone.

The Challenges of Owning a Horse with Navicular Disease
Owning a horse with Navicular Disease can be quite challenging due to its impact on the animal’s performance and overall quality of life. As the condition causes discomfort and lameness, the horse may experience a decline in its athletic abilities and daily activities.
This may limit the horse’s suitability for various disciplines such as dressage, jumping, or trail riding. Furthermore, the pain and limitations resulting from the disease can lead to a diminished quality of life, affecting the horse’s overall happiness and well-being.
Financial aspects: veterinary care and treatments
The financial aspects of managing a horse with Navicular Disease can be substantial, as the condition often requires ongoing veterinary care and treatment. Expenses may include diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans, and regular visits from a farrier to ensure proper hoof care.
Additionally, treatment options like medications, corrective shoeing, and alternative therapies can be costly. The financial commitment of managing a horse with this condition should be carefully considered when deciding whether to own a horse with Navicular Disease.
The emotional toll on the owner
Beyond the practical challenges, owning a horse with Navicular Disease can take an emotional toll on the owner. Watching a beloved equine companion struggle with pain and discomfort can be distressing, and the uncertainty of the disease’s progression can be anxiety-inducing.
Additionally, the potential need to make difficult decisions regarding the horse’s future, such as retiring from competition or considering humane euthanasia, can weigh heavily on the owner’s emotions. It is essential for potential horse owners to be prepared for the emotional challenges of managing a horse with Navicular Disease.
Treatment and Management Options
Navigating the complexities of Navicular Disease requires a thorough understanding of the various treatment and management options available. Owners must explore both traditional and alternative therapies to find the most suitable approach for their horse’s specific needs.
Traditional treatments and therapies
When it comes to treating and managing Navicular Disease, several traditional options can help alleviate symptoms and improve a horse’s quality of life. These may include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as phenylbutazone or flunixin meglumine, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corrective shoeing: A skilled farrier can provide specialized shoeing techniques and adjustments to redistribute pressure, promote proper hoof balance, and alleviate discomfort.
- Joint injections: Veterinarians may administer corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid directly into the affected joint to decrease inflammation and improve joint function.
- Rest and controlled exercise: Limiting strenuous activities while incorporating controlled exercise, such as hand-walking or light riding, can help maintain mobility without exacerbating the condition.
Alternative and complementary therapies
In addition to traditional treatments, alternative and complementary therapies may provide additional support in managing Navicular Disease:
- Acupuncture: By stimulating specific points on the horse’s body, acupuncture can help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation.
- Chiropractic care: Regular chiropractic adjustments can help maintain alignment and balance in the horse’s body, potentially alleviating stress on the affected areas.
- Shockwave therapy: This non-invasive treatment uses high-energy sound waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain in the affected tissues.
- Nutritional supplements: Providing supplements that support joint health, such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and MSM, may offer some benefits in managing Navicular Disease.
Potential Outcomes and Prognosis
The outcome and prognosis for a horse with Navicular syndrome depend on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the horse’s individual response to treatment, and the owner’s commitment to proper management. In some cases, horses may continue to perform at a lower level or transition to a different discipline with appropriate treatment and care.
However, others may need to retire from athletic activities altogether. Early intervention and a comprehensive management plan can significantly impact the horse’s prognosis and quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with an experienced veterinarian and farrier to develop the best treatment plan for your horse’s specific needs.

Factors to Consider Before Buying a Horse with Navicular Disease
Before purchasing a horse with Navicular Disease, it’s crucial to evaluate your goals and expectations for the animal. Consider whether you plan to use the horse for leisure riding, competition, or breeding purposes.
Keep in mind that a horse with this condition may not be suitable for high-performance activities or strenuous disciplines. It’s essential to determine if your goals align with the horse’s abilities and limitations due to Navicular syndrome.
Availability of appropriate care and resources
Proper care and management are critical for a horse with Navicular. Before making a purchase, ensure you have access to the necessary resources, including an experienced veterinarian, a skilled farrier, and appropriate facilities for the horse’s ongoing care.
Consider the financial commitment involved in managing this condition, including veterinary expenses, treatments, and specialized shoeing. Being prepared and knowledgeable about the required care will help you make an informed decision about purchasing a horse with Navicular Disease.
Assessing the severity of the disease in the specific horse
The severity of Navicular Disease can vary greatly from one horse to another. Before purchasing a horse with this condition, it’s essential to assess the specific animal’s situation. Consult with a veterinarian to obtain a thorough evaluation, including diagnostic imaging, to determine the extent of the disease and the horse’s current condition.
Understanding the severity of the disease in the particular horse will help you gauge the potential challenges and limitations you may face as an owner, allowing you to make the best decision for your circumstances.
The Positives of Owning a Horse with Navicular Disease
While Navicular Disease can present challenges, it’s important to recognize that many horses with this condition can lead fulfilling lives with the right management and treatment. Advances in veterinary care and a better understanding of the disease have led to improved treatment options and successful management strategies. Owning a horse with Navicular Disease can be rewarding, as you may witness your horse’s improvement and continued ability to enjoy various activities under your care.
Bonding
Owning a horse with Navicular Disease can also foster a strong bond between the horse and owner. The time and effort invested in caring for a horse with this condition can lead to a deep and meaningful connection. The unique challenges of managing Navicular Disease can inspire a sense of partnership and trust as you work together to overcome obstacles and support your horse’s well-being.
Raising awareness of the disease
As an owner of a horse with Navicular Disease, you can play a vital role in advocating for and raising awareness about this condition. Sharing your experiences, knowledge, and insights can help educate others about the realities of Navicular Disease and the importance of proper management.
By raising awareness, you can contribute to a more compassionate and informed equine community, encouraging responsible ownership and promoting better care for all horses affected by this condition.
FAQs
Should a horse with navicular be ridden?
A horse with navicular can be ridden, but the intensity and duration of exercise should be carefully monitored. Light riding or low-impact activities may be appropriate, depending on the severity of the condition and the horse’s response to treatment. Always consult with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable riding plan for your horse’s specific needs.
Do hoof boots help with navicular disease?
Hoof boots can help horses with navicular disease by providing cushioning, support, and shock absorption, which may alleviate discomfort and promote proper hoof mechanics. However, the effectiveness of hoof boots depends on the individual horse and the severity of the condition. Consult with a veterinarian and farrier to determine if hoof boots are appropriate for your horse’s needs.
Related articles:
- If Your Horse has Thrush Can You Still Ride it?
- Horseshoes: Why Horses Need Them Plus Facts, Uses, and Types
We hope that the blog is informative, looking forward to reading your thoughts in the comments.
Meet Miles Henry
An avid equestrian and seasoned racehorse owner, Miles Henry brings his extensive experience to the equine world, proudly associating with the AQHA, The Jockey Club, and various other equine organizations. Beyond the racetrack, Miles is an accomplished author, having published various books about horses, and is a recognized authority in the field, with his work cited in multiple publications.
🔗 Connect with Miles:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube: Check out race highlights, horse care tips, and more!

